Tuberculosis, commonly known as TB, is an infectious disease that mostly affects the lungs. It can also affect other organs, such as the kidneys, brain, or spine. It remained a major cause of death worldwide in the past and was claimed to be an epidemic by WHO.
With time as living conditions have improved and due to medical advancements, the occurrence of TB has minimized in developed nations. It is reported as the 13th leading cause of death worldwide and the second leading infectious disease that kills after Covid-19.
In 2020, WHO estimates that 10 million people contracted TB worldwide while 1.5 million died due to it.TB remains a major cause of concern worldwide, especially in Asia. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 7,174 cases of TB were reported in the US in 2020. It can be difficult to treat tuberculosis due to antibiotic resistance; however, treatment is available.
What Causes Tuberculosis
Since tuberculosis is an infectious disease, the bacteria can spread through air particles. However, it doesn’t spread easily. Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the bacteria that is the main cause of tuberculosis in the affected people. Only spending long hours with someone who has TB can be a reason for you to catch the disease.
Anyone who has contracted tuberculosis but doesn’t have any symptoms of the disease has latent or inactive tuberculosis. It may appear to be cured, but it is dormant in the body. Active tuberculosis is when you have the disease and show symptoms of it.
Kinds of Tuberculosis
Apart from active and latent tuberculosis, there are other kinds of TB as well, which depend on the organs it affects in the body. A person can contract extrapulmonary tuberculosis, which means the disease is contracted outside the lungs.
Another kind of tuberculosis is systemic military tuberculosis which can spread to other parts of the body and lead to other diseases such as meningitis, Pott’s disease, hepatitis, sterile pyuria, or lymphadenitis.
Symptoms of Tuberculosis
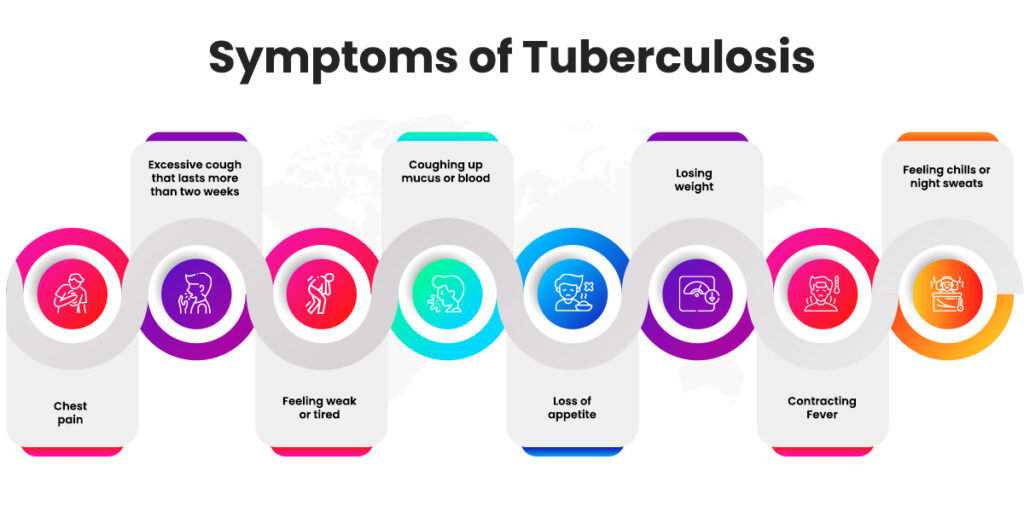
There are no symptoms in the case of inactive tuberculosis. In the case of active tuberculosis, a person may experience the following:
- Chest pain
- Excessive cough that lasts more than two weeks
- Feeling weak or tired
- Coughing up mucus or blood
- Loss of appetite
- Losing weight
- Contracting fever
- Feeling chills or night sweats
Symptoms can also occur in other body areas, although the condition mostly affects the lungs. People with weak immune systems are likely to experience bone or joint pain, confusion, seizures, persistent headaches, abdominal pain, and persistent swelling of lymph nodes.
Diagnosis of Tuberculosis
Various screening tests are effective in the diagnosis of Tuberculosis. Your doctor may recommend a blood test called interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA) or Mantoux tuberculin skin test (TST).
The TST is carried out by injecting a purified protein derivative (PPD) under the forearm skin. The healthcare provider will check the injection site after two or three days to complete the diagnosis.
The IGRA test is carried out by evaluating a blood sample from the body in the lab. More tests to diagnose the severity of the condition include chest X-Ray, CT scan service nj, and lung fluid or sputum lab tests.
When to Get Tested?
There are several indications that you should get tested for TB and book digital x-ray services in NJ for a diagnosis. These include:
Spending time in a high-risk setting such as a healthcare facility, shelter, or skilled nursing facility where you are an employee or resident.
- Employed in a mycobacteriology laboratory
- Having a weak immune system and low resistance to illness
- Spending time with someone who has tuberculosis
- Living in TB-intensive regions such as Eastern Europe, Latin America, Russia, Asia, the Caribbean, and Africa
- Habitually injecting recreational drugs
- Other people at risk of tuberculosis include:
- People who have diabetes, kidney disease, or other long-term chronic illness
- People who have received organ transplants
- Babies and children with an immature immune system
- People undergoing chemotherapy for cancer or receiving another treatment for immune system disorders.
Tuberculosis can easily affect people who have a weak immune system. Reasons that weaken the immune system include the following:
Smoking
The risk of developing TB increases in people who smoke or engage in passive smoking. Smoking also makes it more difficult to treat and the condition is more likely to return even after the complete course of antibiotics.
HIV
Doctors believe people who have HIV are at a higher risk of contracting tuberculosis and may experience severe symptoms. Treatment of TB in persons with HIV is more complex and requires a comprehensive treatment plan keeping in mind both diseases.
Treatment for Tuberculosis
Different drugs are available for treating tuberculosis, such as Isoniazid, Ethambutol, Rifapentine, Pyrazinamide, or Rifampin. All the medicines prescribed by the doctor are essential for killing all the bacteria and should be taken for the entire duration they are prescribed, which can be up to nine months.
The type of antibiotic and length of treatment depends on a number of factors. It is based on whether they are suffering from active or inactive tuberculosis, the area of infection, the person’s overall health status and age, and whether the strain is drug resistant.
In the case where the person has developed a drug-resistant strain, the treatment can be complex involving several drugs. Leaving the treatment halfway or as soon as the symptoms disappear can prevent killing the bacteria entirely. These bacteria that survive become resistant to medication leading to drug-resistant tuberculosis.
Antibiotics for tuberculosis can cause side effects or complications in some people. Anyone undergoing treatment can experience an upset stomach, nausea, itchy skin or rashes, yellow eyes, or dark-colored urine.
How Soon Can You Start Feeling Better
Contrary to popular belief, tuberculosis is curable. However, it can take some time. You can start feeling better in a few weeks, after which symptoms will start decreasing, and you will feel like having your energy back. The complete treatment takes six to nine months before the person can feel like themselves again.
How to Prevent Spreading Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis does not spread easily, and it takes a long time before someone can contract it. Nevertheless, you can follow some guidelines to prevent the spread of the disease, such as:
- Covering your mouth when coughing
- Maintaining a safe distance from other people
- Frequently washing your hands thoroughly
- Taking all the medication as prescribed
- Not attending school or work until recommended by the healthcare practitioner
Other ways to prevent the spread of tuberculosis include getting a diagnosis as soon as the first symptoms appear and starting treatment immediately. You can also keep your rooms ventilated and wear a mask in social gatherings.
Summary
Tuberculosis is a curable disease albeit it can take some time. However, in the absence of treatment, it can be fatal. Since tuberculosis spreads throughout the body, it can cause other complications as well in the metabolic function and cardiovascular system. If not treated rightly, TB can lead to sepsis, which is a kind of infection that’s life-threatening.
Appropriate treatment for tuberculosis patients is vital to living a healthy life again otherwise it can potentially become deadly. Early detection through full-body CT scan services can lead to early intervention and successful treatment that causes little to no complications.
People who have a high risk of contracting the disease or feel they are displaying the symptoms should immediately book a consultation with their health care practitioner and get their relevant tests as recommended. Digital x-ray services in NJ from a reputable diagnostic center like AQMDI can help in the early and timely diagnosis of TB.

